Complete Guide About Amazon Inspector will be described in this article.
Complete Guide About Amazon Inspector In 2024
In this article, you can know about Amazon Inspector here are the details below;
Whether we realize it or not, there could be security holes in the servers, network infrastructure, and applications that we use in our production and staging environments. Let’s take an example where we have a misconfigured Redis server in our staging environment and we unintentionally left the port open, making it accessible to anything outside of the VPC. We might discover that this cache server is targeting additional servers in addition to its original purpose, depending on how quickly this server is compromised (in minutes or hours). It is currently best to assume that additional computers connected to this server may also have been compromised and that this server can no longer be trusted. We should audit and guarantee the total security of our systems because this is something that we all want to prevent. Using vulnerability scanning technologies, which search for pertinent weaknesses in our systems, is one approach to stop these problems from happening.
Using Amazon Inspector is one of the more convenient ways to integrate automatic security assessments if we already have container images in ECR and EC2 instances operating in our AWS account. Along with other significant improvements, the new edition of Amazon Inspector now features continuous automatic scans in favor of the previous method’s sporadic and human scanning. The neat thing about this is that whenever a “change” is made, Amazon Inspector immediately finds the EC2 instances and container images in our account and runs the assessment scan. Naturally, upon discovery, all recently discovered instances and container images are also inspected. Long-term, this new method of leveraging Amazon Inspector makes things much more scalable and useful.
Detecting and Scanning Container Images for Vulnerabilities
We simply establish a new ECR repository and push a sample vulnerable container image, such as one that contains DVWA (D*** Vulnerable Web Application), to test Amazon Inspector’s ability to detect and automatically scan container images.
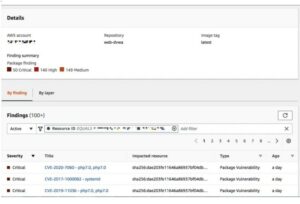
After a short while, we may observe that Amazon Inspector has identified 50 critical flaws.
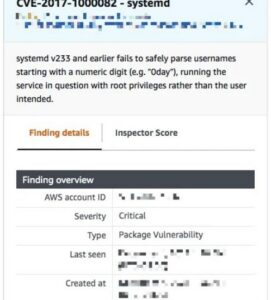
We can view additional information about one of the reported concerns by clicking the title link.
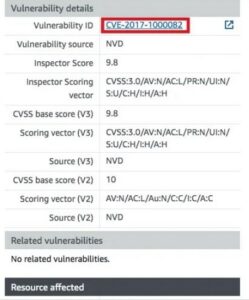
There should be a link that opens a reference with further details about this vulnerability if we scroll down a little.
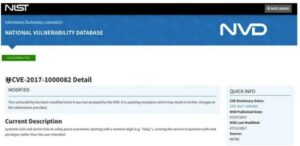
The following page should appear after clicking the Vulnerability ID link:
Detecting and Scanning EC2 Instances for Vulnerabilities
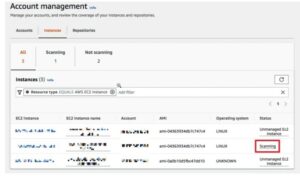
We just start any instance in an already-existing VPC to evaluate Amazon Inspector’s ability to identify and automatically scan EC2 instances. In this case, we used the Amazon Linux 2 image to start a fresh Cloud9 instance. The newly launched instance should appear in the Amazon Inspector console’s Account management page (as well as other pertinent pages) a few minutes after it was launched.
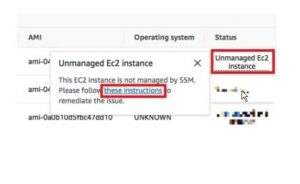
Click “Unmanaged EC2 instance” and then “these instructions” if Amazon Inspector is unable to identify the target instance (e.g., Status = “Unmanaged EC2 instance”).
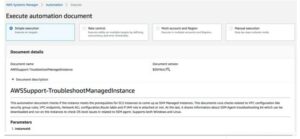
This ought to launch the Systems Manager page for the Execute automation document, which we’ll need to troubleshoot the setup and settings.
All we have to do is enter the instance ID and select “Execute.” The automation that has been run should provide us with the debugging data we require to correct the setup in a few minutes.
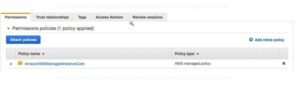
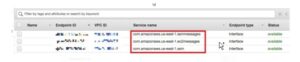
First, we must make sure that the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy is tied to the IAM role that the instance is using. We accomplish this by attaching the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy to a newly created IAM role, or by utilizing an already-existing one. The pertinent VPC endpoints must also be set in the VPC that houses the target instance.
Repeat the Systems Manager troubleshooting steps, confirm the issues that have already been resolved, and then address the remaining configuration issues that have been reported. When everything is set up correctly, the instance should start to be scanned by Amazon Inspector.
Amazon Inspector 10 instances The vulnerabilities that the scan reported ought to appear after a short while.
When we follow the same procedures as in Part II, when we scanned an image of a vulnerable container, we ought to see a page that looks like the one in the picture below.
Why Should you use Amazon Inspector?
As we can see, it’s easy to get Amazon Inspector to function in our accounts. Setting it up to function with EC2 instances may take a few minutes, but the ongoing evaluation and scan of the resources involved readily repays this effort. We won’t need to manually initiate the additional scans because Amazon Inspector will automatically identify any changes to the EC2 instance and conduct them, just like it does with Amazon Inspector Classic. Also check How To Cancel Amazon Prime
Advantages:
Automatic Scanner:
Amazon Inspector finds compliance problems and security flaws automatically. This lets you get faster results by automating tasks that would otherwise need human labor.
Compliance Controls:
Organizations can need to adhere to particular regulations. Amazon Inspector offers compliance controls to guarantee that workloads and AWS services adhere to these specifications.
Comprehensive Reporting:
Based on the scanner’s findings, Amazon Inspector provides extensive reports. These reports offer suggestions for resolving the compliance problems and security vulnerabilities that have been found, as well as assistance in understanding them.
Easy Integration:
Integrating Amazon Inspector with your current AWS infrastructure is simple. This lets you immediately launch the scanner and guarantees compatibility with your present AWS environment.
Disadvantages:
Customization Challenges:
There can be restrictions on the customization options available for Amazon Inspector. Because of this, some users might have to rely on extra resources or techniques to fulfill particular needs.
Processing Time:
Prolonged processing times may be caused by the comprehensive scans that Amazon Inspector may need. Performance problems in extensive applications or infrastructures may result from this.
Additional Cost:
The cost of the service should be taken into account while using Amazon Inspector. Depending on the frequency of scanning, quantity of resources scanned, and reporting requirements, the cost of using the service may change.
You can use Amazon Inspector, a useful tool, to examine your AWS apps and infrastructure for security flaws and compliance problems. Benefits include easy integration, extensive reporting, compliance controls, and automatic scanning.
It would be beneficial if you took into account some of its drawbacks, such as difficulties with personalization, processing time, and possible extra expenses.
It’s vital to take into account additional options in addition to Amazon Inspector.
Popular alternatives to Amazon Inspector:
Nessus:
Tenable offers a vulnerability scanner called Nessus. It is employed to find security holes in networks’ worth of systems and applications. Nessus can scan a wide range of common vulnerabilities and has access to a vast vulnerability database. It also offers a wide range of the integration possibilities and customization choices. Also check What Is Amazon Digital Charge
Qualys:
Qualys is a security and compliance solution that operates on the cloud. It is employed to identify network and application layer security flaws as well as compliance problems. In addition to providing a thorough scanner, Qualys can verify for compliance with a number of industry standards (PCI DSS, HIPAA, etc.). It also offers several integration options and efficient reporting functions.
OpenVAS:
An open-source vulnerability scanner, OpenVAS stands for Open Vulnerability Assessment System. It is employed to find security holes in networks’ worth of systems and applications. OpenVAS may be tailored to the needs of the user and has a large vulnerability database. Reporting and integration features are also included.
Rapid7 InsightVM:
This is a risk management and network security service. It is employed in the analysis of risks, detection of security flaws, and system compliance checks. Rich reporting options and an extensive scanner are provided by Rapid7 InsightVM. Additionally, it offers efficient workflow tools to assist users in organizing and controlling the remediation process.
Conclusion:
There are benefits drawbacks associated with each of these substitute services in relation to Amazon Inspector. While some services might be more affordable or simpler to integrate, others might provide more features and customization choices. It is crucial to take into account your needs, financial constraints, and top priorities when deciding which service is right for you.